Emergency Bleeding Control: How to Stop Life-Threatening Bleeds
We’ve all been there—a slip of the kitchen knife or a scraped knee on the playground. Usually, a quick Band-Aid and a little bit of “toughing it out” does the trick. But what happens when the situation is much more serious? What if you’re at work and a major accident occurs?
In those moments, the adrenaline hits, your heart races, and suddenly, those first few seconds feel like an eternity. Honestly, it’s terrifying. But here’s the truth: you don’t have to be a surgeon to save a life. You just need to know exactly how to stop bleeding before professional help arrives. At Safety Is A Mindset, we believe that empowerment comes from preparation.
If you’re a business owner here in Greenville, TX, or managing a team in a high-risk industry, having this knowledge isn’t just a “nice to have”—it’s a critical part of your workplace safety training.
1. Start with Direct Manual Pressure
It sounds simple, and that’s because it is. If someone is bleeding, your first instinct should be to grab the cleanest cloth available (or even your bare hands if you have gloves) and press down hard.
- Find the source: You need to see exactly where the blood is coming from.
- Firm pressure: Use both hands if you have to. Don’t keep lifting the cloth to check if it has stopped; you’ll break the clots that are trying to form.
- Keep it up: Maintain pressure until EMS arrives or the bleeding is clearly under control.
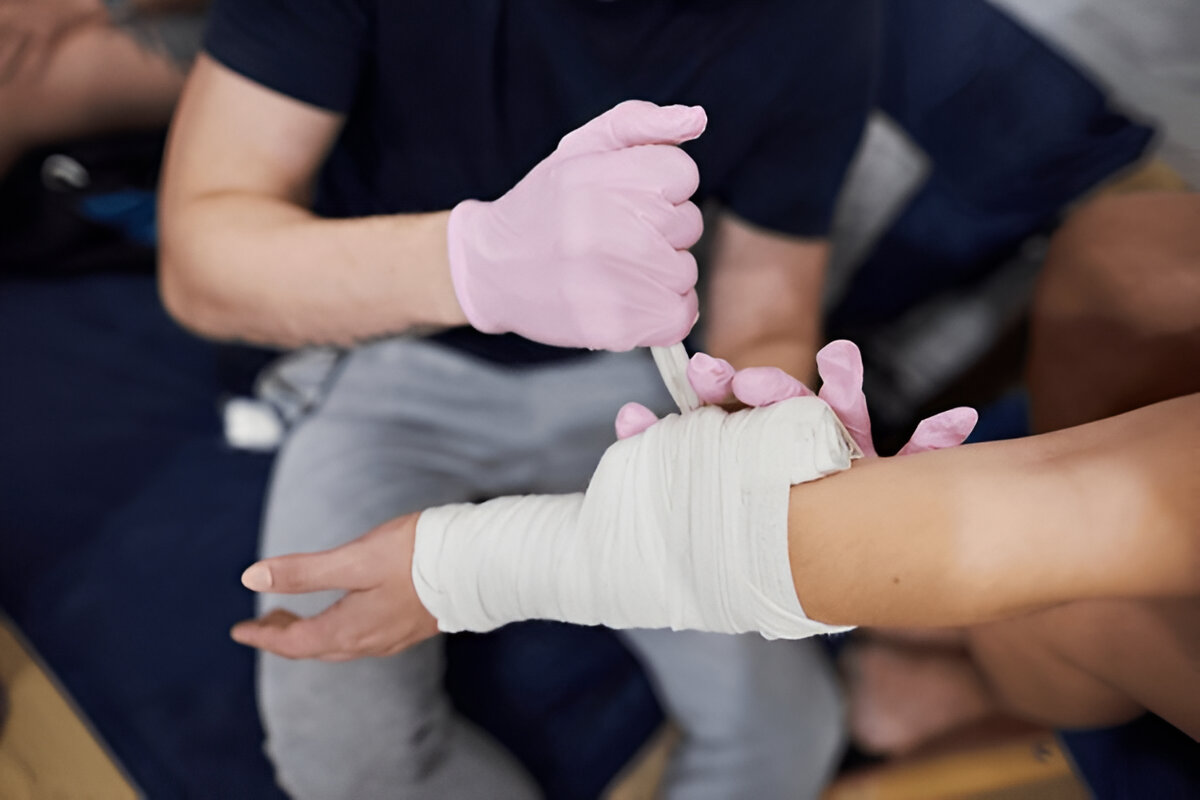
2. The Power of Bandaging
Once you’ve slowed down the initial flow, a proper bandage helps maintain that pressure, allowing you to focus on other tasks—such as calling 911 or calming the victim. Our first aid CPR classes guide you through the nuances of bandaging different parts of the body, ensuring the wrap is tight enough to provide support without cutting off all circulation to healthy tissue.
3. When to Use a Tourniquet
There’s a lot of old-school myths about tourniquets being a “last resort” that will definitely lead to limb loss. Modern science tells a different story. If you’re dealing with life-threatening bleeding on an arm or leg that doesn’t stop with pressure, a tourniquet is a literal lifesaver.
- High and Tight: Place the tourniquet 2-3 inches above the wound, but never on a joint.
- Twist until it stops: You need to tighten it until the bright red, spurting blood stops completely. Yes, it will hurt the person, but it’s better than the alternative.
- Commercial vs. Improvised: While we teach how to use improvised items in our stop the bleed training, having a commercial windlass tourniquet in your kit is always the gold standard.
4. Recognizing the Signs of Shock
Bleeding isn’t just about the wound you can see; it’s about what’s happening inside the body. When someone loses too much blood, they go into shock. Look for:
- Pale, cold, or clammy skin.
- Rapid breathing or a weak pulse.
- Confusion or extreme restlessness.
If you see these signs, keep them warm, keep them still, and keep talking to them until help arrives.
Why Greenville Businesses are Choosing AVERT Training
Sometimes, the cause of the bleeding isn’t an accident—it’s intentional violence. It’s a heavy topic, but we can’t ignore it. That’s why many organizations are moving beyond standard first aid and opting for AVERT training (Active Violence Emergency Response Training).
AVERT is unique because it combines with emergency “stop the bleed” techniques. In a crisis, you may be the “immediate responder” before paramedics can safely enter the scene.
Whether you are in , , or even , knowing how to transition from escaping a threat to treating a victim is the ultimate safety mindset.
Real Skills for Real People
You don’t need a medical degree to make a difference. Our is designed for everyday people—office managers, teachers, and shop foremen. We use scenario-based videos and hands-on practice so that when the “real thing” happens, your muscle memory takes over.
Quick Summary of Our Training Options in Texas: | Feature | CPR & AED Course | AVERT Training | | :— | :— | :— | | Duration | 8 Hours | 4 Hours | | Focus | Medical emergencies, SCA, Choking | Active violence, Situational awareness | | Bleeding Control | Basic internal/external | Advanced “Stop the Bleed” | | Certification | 2 Years | 2 Years |
Take the Next Step for Your Team
Look, we all hope we never have to use these skills. But “hoping” isn’t a safety plan. Whether you’re looking for onsite safety training for your staff or a CPR AED certification for yourself, we’re here to help you get prepared.






Comments are closed